A car engine needs an initial help to turn at its crankshaft to initiate revolution before combustion occurs and the engine can run on itself. On many vehicles, this is done by an electric motor, called a starter, which turns a gear at the flywheel.
It is an electric motor that starts the car
During a start, the initial torque produced by the starter (which is an electric motor, which torque is multiplied by the starter pinion – flywheel gear) must be sufficient to overcome compression and inertia, friction, and other loads. The starter motor itself requires quite an amount of electricity to operate. To successfully start an engine, there must be enough stored energy in a car battery to turn the starter. Here we will learn how to check a battery with only one tool.
A car battery ages with time and use, and its stored energy capacity depletes over years. Without due attention to the declining reserve power, we may get caught on one cold morning where the battery is unable to provide enough power to start the car’s engine.
Monitoring battery voltage at times is good idea
Monitoring the battery voltage at specific condition can help to prevent the unexpected condition. By this we mean watching the battery voltage to get a rough prediction about the battery capability to start the engine. Thus, we can give a quite reliable check using only one tool, which is a voltmeter.
There are 3 (three) conditions at which a battery voltage can be checked to help giving the rough prediction on battery condition.
Required (recommended) tool: a digital voltmeter such as the Fluke 77-4 Automotive Digital Multimeter.
A digital multimeter
A reliable in-vehicle vehicle battery voltage monitoring device may also be used, such as the ScanGauge II, which also serves as a ECU reader.
This tip is pretty useful for battery which has been in a vehicle for one or a few years and there is doubt whether it is about the time to replace the battery.
 Here are the battery tests to do:
Here are the battery tests to do:
1. Battery voltage with engine off.
This is a test to check remaining battery voltage when the battery is not being charged.
How to do it: If the engine has just been turned off, turn on the headlights for about 20 to 30 seconds to remove surface charge, and turn them off. If the engine has been off for a few hours, just proceed with the followign step.
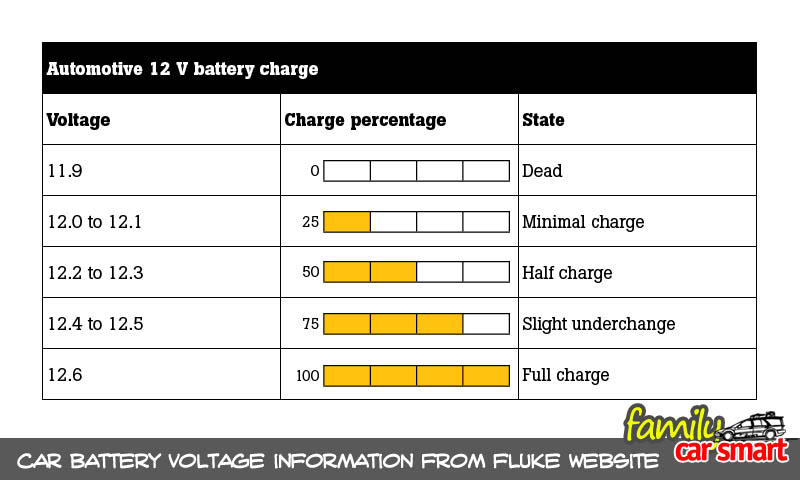
Check the battery voltage. If it is less than 12.5 volt, the battery may need further examination or replaced.
Fluke instrument website has some information on this voltage reading. The following is a chart from Fluke. Further examination on Fluke’s page might be useful.
2. Minimum battery voltage during starting.
During starting, the starter pulls current from the battery which will drop the battery voltage during the starting sequence. The voltage drop (or as we measure: the lowest battery voltage during a start) illustrates the amount of energy left in a battery for starting. A voltage which drops lower than the limit may the stored energy is insufficient or nearly insufficient to start the engine.
How to do it: With the voltmeter connected (or the in-vehicle device set to measure voltage), start the engine. Watch the lowest measured voltage. It should be no less than 10.8 volt during starting.
If it is lower, the battery may be getting weak. The engine may still start though, but a further system check or battery replacement may be necessary. This may also mean that a new battery may be needed soon.
This is much easier with an external voltmeter that has a capability to register lowest /highest measured voltage.
3. Measuring voltage with engine running.
This test serves to see whether the charging circuit works to charge the battery. To do this, just start the engine. After the engine starts, wait a few seconds. The voltmeter should show voltage between 13.3 and 15.3 volt. A normal charging would show between 13.8 and 14.2 volts. If it is below 13.3 volt, the battery may not be charged sufficiently and this may lead to difficulty during starting later. A voltage lower than 13.3 volt may indicate a problem with the car charging system. An alternator replacement may be required.
While the above 3 tests are quite reliable to predict battery condition, or whether a battery is nearing replacement, other factors may also affect battery status. Thus this article may serve as a rough illustration on reliability of starting the car engine can make. The standard voltages may vary among cars, too.
There is also a method to predict battery condition without any tool. This method will be covered later in another article.
A video will soon be uploaded on how the tests are done using a digital multimeter.
Of course this article is not a complete for solving car battery problems. But is it useful for you? Do you have any suggestion? Please fill in the comment below.
Thank you.