This is an old tip for a difficult-to-start vehicle which still applies today. Problem: the car has difficulty to start. The starter cranks but it never gets to turn the engine fast or long enough to start. Repeated attempts give the same thing. The starter cranks, but fails to get engine running. The battery is still quite new and no wiring problem has ever occurred. It easily brings out the question whether it is a starter solenoid or battery problem.
Car starting basics
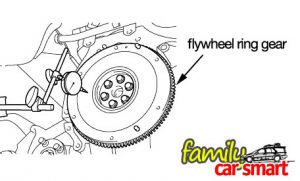 An electric motor, called the starter motor starts the car. It has a small gear that meshes with a much larger gear on the engine’s flywheel to turn the engine. The larger flywheel gear multiplies the torque from the starter motor. During
An electric motor, called the starter motor starts the car. It has a small gear that meshes with a much larger gear on the engine’s flywheel to turn the engine. The larger flywheel gear multiplies the torque from the starter motor. During
starting, the starter turns the flywheel before combustion is made and the engine can run on itself.
The high power required by starter motor
While turning the engine to start, the starter motor must overcome combustion chamber compression and engine component’s inertia. To do this, the starter motor must have significant power. Even with gear ratio torque multiplication on the starter-flywheel, it still requires a lot of power.
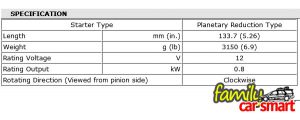
The starter motor is indeed a high power electric motor. A typical starter for a 1.3 liter engine is rated at 0.8 kW at 12V (see specification in picture). This is quite a big motor, which size is easily imagined by comparing it to our power drill or a home appliance. A larger engine certainly needs a larger starter motor, and larger stored power, which means a larger battery (for an article about where car electricity comes from, see here).
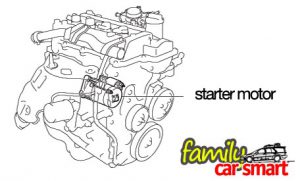
The current draw is huge too.
A starter motor rated 0.8 kW starter motor at 12 V draws current of 66 amperes during starting an engine (actual current draw varies according to conditions). To carry this much current to the starter during starting, a heavy gauge wire is required.
Since the current to the starter is controlled by the car ignition switch, a starter relay /solenoid is used to allow the car ignition key to serve only as a provider of start signal. Therewith, the high current does not need to pass through the ignition switch.

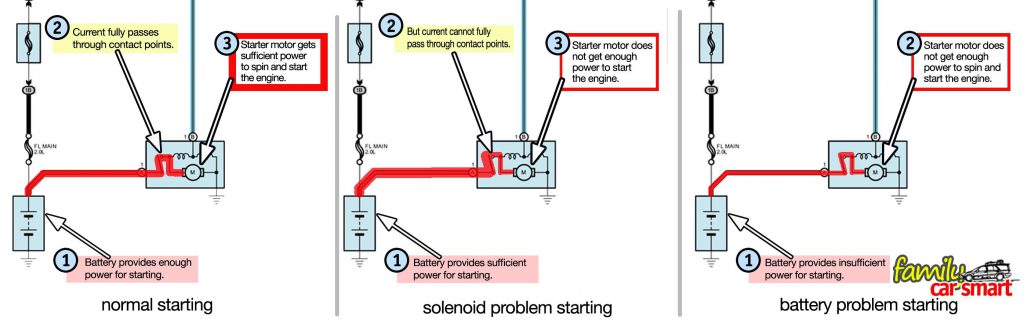
During start, the ignition switch or key actuates the solenoid, which then pulls the solenoid contacts to pass current to the motor. If everything is normal, the contacts can pass current sufficiently as needed by the motor.
A very large current must pass from the battery to the starter motor windings. The starter solenoid passes this current through contacts (no. 2 in the picture).
The solenoid starter problem
Due to repeated use, these contacts can get dirty from sparks generated during its work. Overtime, the dirty contacts create resistance which restricts current from passing through. When the resistance becomes high enough, the contacts will fail to pass sufficient current to the starter motor. A bottleneck is created, choking the motor of current.
When this happens, even though the battery can provide enough power to start, the starter motor is unable to get enough current to work, because the current path is restricted at the solenoid contacts. The conditions with normal starting, low battery power, and starting with solenoid contact issue are shown in the following picture:
How to check which one causes the problem with any car electrical equipment
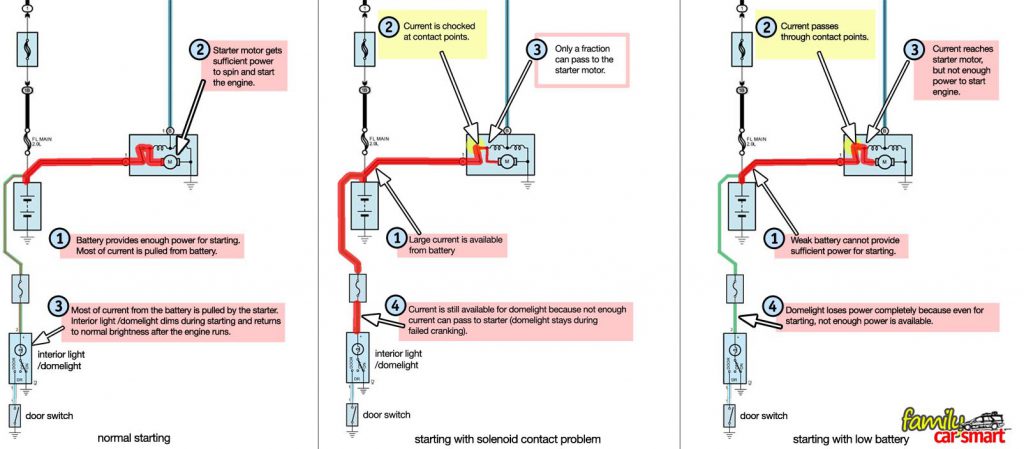
The starter pulls a very large current during starting. Just like water flowing in a pipe, electricity also tends to flow toward the largest flow, leaving other lines short of current. With this principle, any car electrical equipment can be used to test whether the solenoid is the source of problem.
An easy and safe way is to use the domelight. Turn the domelight on, and try to start the engine. In the event:
(1) The starter just halts during starting and the domelight stays bright, the problem is bad solenoid contacts. The solenoid should be replaced.
(2) The starter just halts during starting and the domelight dims or turns off, the problem is weak battery. Check battery condition. Replace when necessary.
These can be seen in the following pictures, with normal starting conditions shown as comparison.
This is actually very simple knowledge, most of us must have known, yet is very practical and useful. I found this tip in a Toyota owner’s manual. Thumbs up for Toyota to include this practical tip which is very useful for car owners.
If you have any comment or suggestions, please leave in the box below.
Thank you.